How is our voice produced? We use our voices all the time, every day, to communicate with family, friends, and colleagues, never really thinking about how it is produced. Like driving, after a while, becomes second nature and we don’t consciously think about the process. But a little knowledge can be a powerful thing and to understand the mechanisms of our voice is very useful – particularly to maintain a healthy and effective voice.
Here is an overview which describes the body parts and their functions in producing our speaking and singing voices:
There are basically three main components:
The Power Source: The Lungs
The Vibrator: The Voice Box
The Resonator: The Throat, Nose, Mouth, and Sinuses
The Power Source: The power for your voice comes from air that you exhale. When we inhale, the diaphragm lowers and the rib cage expands, drawing air into the lungs. As we exhale, the process reverses and air exits the lungs, creating an airstream in the trachea. This airstream provides the energy for the vocal folds in the voice box to produce sound. The stronger the airstream, the stronger the voice. Give your voice good breath support to create a steady strong airstream that helps you make clear sounds.
The Vibrator: The larynx (or voice box) sits on top of the windpipe. It contains two vocal folds (also known as vocal cords) that open during breathing and close during swallowing and voice production. When we produce voice, the airstream passes between the two vocal folds that have come together. These folds are soft and are set into vibration by the passing airstream. They vibrate very fast from 100 to 1000 times per second, depending on the pitch of the sound we make. Pitch is determined by the length and tension of the vocal folds, which are controlled by muscles in the larynx.
The Resonator: By themselves, the vocal folds produce a noise that sounds like simple buzzing, much like the mouthpiece on a trumpet. All of the structure above the folds, including the throat, nose, and mouth, are part of the resonator system. We can compare these structures to those of a horn or trumpet. The buzzing sound created by vocal fold vibration is changed by the shape of the resonator tract to produce our unique human sound.
When our voices are healthy, the three main parts work in harmony to provide a balanced voice during speaking and singing.
Vocal Folds:
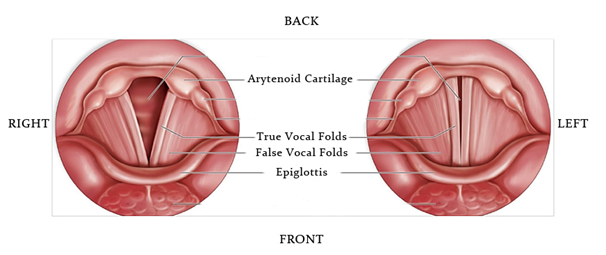
The primary function of the vocal cords and the surrounding supporting muscles, nerves and cartilages is to protect our airway from foreign bodies entering and causing us to choke. It is their secondary function to make noise allowing us to communicate, speak and sing.